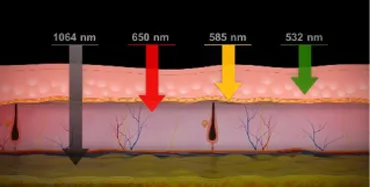
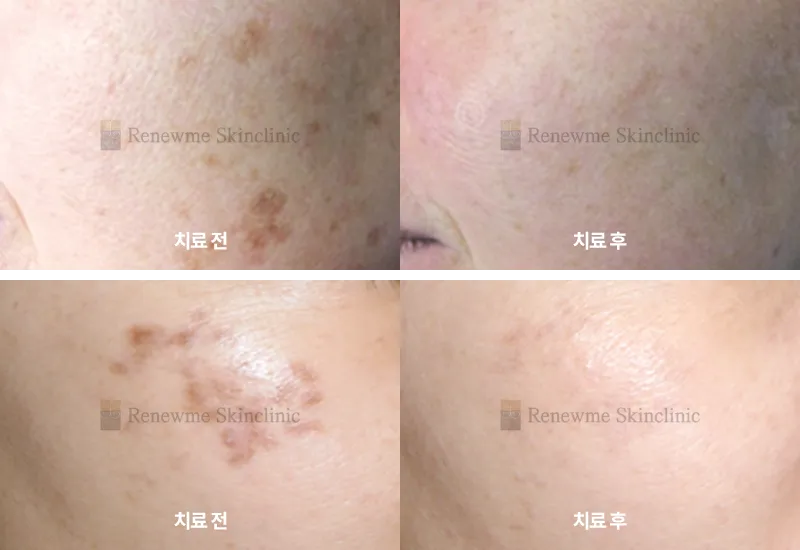
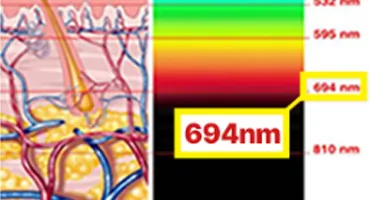
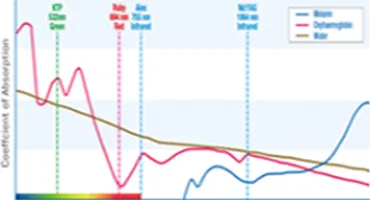
Causes of Pigmentation
The primary cause of pigmentation is melanocytes
Melanocytes, located in the deepest part of the epidermis, distribute pigment that is essential to our skin through a branch-shaped process. Melanocytes protect our skin from UV rays but when exposed excessively to UV rays, the number and size of melanocytes increase rapidly, producing a large amount of melanin. When the inflamed area is exposed to UV rays, more melanocytes settle on the dermis, resulting in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.
Consequently, uneven distribution of melanin can cause uneven brown pigmentation. In cases of skin inflammation, not only the epidermis but also the dermis can be damaged and damaged melanocytes subside toward the dermis.
When the inflammation area is exposed to UV rays, more amount of melanocytes subside on the dermis, resulting in post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation.